Whenever you’re told to keep out of the sun, keep in mind that you are also depriving your body of amazing vitamin D benefits. The sun is the optimal source of vitamin D absorption, providing it naturally in a form the body can fully utilize. In recent years, most people have been found to have vitamin D deficiencies. This is the result of avoiding sunshine by either keeping out of the sun or applying sunscreen lotions. Vitamin D boosts the body’s ability to fight viral infections like the common flu. In one study, even low dose vitamin D offered extreme protection against all flu strains — slashing your risk by almost half. It also helps the immune system to fight upper respiratory diseases. This magical vitamin wards off infections and helps the body to absorb calcium as well. The body needs calcium to function properly and when there are low levels of calcium, the body has to rely on the calcium content of our bones in order to come up with the calcium it needs. Vitamin D helps the body to absorb more calcium from food so that bones remain healthy. Vitamin D has also been found to help people with asthma and other respiratory diseases to breathe normally. Asthma reduces lung functions to the point that an asthmatic patient has trouble breathing. Vitamin D prevents the slow decline in the ability to breath. Recent studies show that there is a link between cancer and low levels of vitamin D. More studies show that vitamin D can play a significant role in the prevention of prostate cancer and other types of cancer as well. Studies also show that Vitamin D can possibly be used in the treatment of diabetes, schizophrenia, hypertension and many other medical conditions. There are not many foods that have sufficient quantities of vitamin D to keep a person healthy. In addition, it is a challenge to absorb adequate amounts of vitamin D during the winter and fall months in most locations. In order to satisfy the body’s need and experience vitamin D benefits, this vitamin needs to be taken as a dietary supplement on a daily basis when optimal sun conditions are not met. 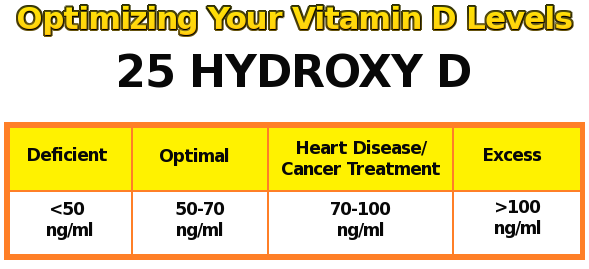 Vitamin D deficiency is quite common, and a growing list of diseases and conditions are being linked with it. Regular sun exposure, without sunscreen, causes your skin to produce vitamin D naturally. But how much sun do you need? You’ve probably seen some vague guidelines, recommending “a few minutes every day.” But these recommendations are far too general to be useful. The amount of sun you need to meet your vitamin D requirements varies hugely, depending on your location, your skin type, the time of year, the time of day, and even the atmospheric conditions. The Vitamin D/UV Calculator Scientists at the Norwegian Institute for Air Research have devised a calculator that will take all those factors into consideration and estimate how many minutes of exposure you need for your skin to produce 25 mcg (the equivalent of 1,000 International Units) of vitamin D. It’s not the most user-friendly interface and it is very easy to enter the wrong information. But once you get past the technicalities, it’s very interesting to see how much the answers change when you vary the input. It is also not written for US cities so you can go to this page to find out latitude and longitude of many cites and enter the numbers manually. The easiest way may be to simply google “altitude of [your town]“. Remember to convert it to kilometers. One kilometer is about 3300 feet. If your latitude is 39 S, enter -39. If your longitude is 76 W, enter -76. You’ll also need to enter the time of day you are going out in the sun, expressed as UTC (Greenwich Mean Time). Here is a converter that will convert local time into UTC. The calculator uses a 24 hour clock, so hours from 1 PM to midnight are expressed as 13 to 24. The calculator also wants to know the thickness of the ozone layer. I suggest just setting this one to medium. Be sure to click the radio button next to the entries. They are often not automatically selected when you fill in the values. Keep in mind that the exposure times given are considered enough to maintain healthy vitamin D status. If you are starting out with a vitamin D deficiency, you might need more.
Vitamin D deficiency is quite common, and a growing list of diseases and conditions are being linked with it. Regular sun exposure, without sunscreen, causes your skin to produce vitamin D naturally. But how much sun do you need? You’ve probably seen some vague guidelines, recommending “a few minutes every day.” But these recommendations are far too general to be useful. The amount of sun you need to meet your vitamin D requirements varies hugely, depending on your location, your skin type, the time of year, the time of day, and even the atmospheric conditions. The Vitamin D/UV Calculator Scientists at the Norwegian Institute for Air Research have devised a calculator that will take all those factors into consideration and estimate how many minutes of exposure you need for your skin to produce 25 mcg (the equivalent of 1,000 International Units) of vitamin D. It’s not the most user-friendly interface and it is very easy to enter the wrong information. But once you get past the technicalities, it’s very interesting to see how much the answers change when you vary the input. It is also not written for US cities so you can go to this page to find out latitude and longitude of many cites and enter the numbers manually. The easiest way may be to simply google “altitude of [your town]“. Remember to convert it to kilometers. One kilometer is about 3300 feet. If your latitude is 39 S, enter -39. If your longitude is 76 W, enter -76. You’ll also need to enter the time of day you are going out in the sun, expressed as UTC (Greenwich Mean Time). Here is a converter that will convert local time into UTC. The calculator uses a 24 hour clock, so hours from 1 PM to midnight are expressed as 13 to 24. The calculator also wants to know the thickness of the ozone layer. I suggest just setting this one to medium. Be sure to click the radio button next to the entries. They are often not automatically selected when you fill in the values. Keep in mind that the exposure times given are considered enough to maintain healthy vitamin D status. If you are starting out with a vitamin D deficiency, you might need more.
 Vitamin D deficiency is quite common, and a growing list of diseases and conditions are being linked with it. Regular sun exposure, without sunscreen, causes your skin to produce vitamin D naturally. But how much sun do you need? You’ve probably seen some vague guidelines, recommending “a few minutes every day.” But these recommendations are far too general to be useful. The amount of sun you need to meet your vitamin D requirements varies hugely, depending on your location, your skin type, the time of year, the time of day, and even the atmospheric conditions. The Vitamin D/UV Calculator Scientists at the Norwegian Institute for Air Research have devised a calculator that will take all those factors into consideration and estimate how many minutes of exposure you need for your skin to produce 25 mcg (the equivalent of 1,000 International Units) of vitamin D. It’s not the most user-friendly interface and it is very easy to enter the wrong information. But once you get past the technicalities, it’s very interesting to see how much the answers change when you vary the input. It is also not written for US cities so you can go to this page to find out latitude and longitude of many cites and enter the numbers manually. The easiest way may be to simply google “altitude of [your town]“. Remember to convert it to kilometers. One kilometer is about 3300 feet. If your latitude is 39 S, enter -39. If your longitude is 76 W, enter -76. You’ll also need to enter the time of day you are going out in the sun, expressed as UTC (Greenwich Mean Time). Here is a converter that will convert local time into UTC. The calculator uses a 24 hour clock, so hours from 1 PM to midnight are expressed as 13 to 24. The calculator also wants to know the thickness of the ozone layer. I suggest just setting this one to medium. Be sure to click the radio button next to the entries. They are often not automatically selected when you fill in the values. Keep in mind that the exposure times given are considered enough to maintain healthy vitamin D status. If you are starting out with a vitamin D deficiency, you might need more.
Vitamin D deficiency is quite common, and a growing list of diseases and conditions are being linked with it. Regular sun exposure, without sunscreen, causes your skin to produce vitamin D naturally. But how much sun do you need? You’ve probably seen some vague guidelines, recommending “a few minutes every day.” But these recommendations are far too general to be useful. The amount of sun you need to meet your vitamin D requirements varies hugely, depending on your location, your skin type, the time of year, the time of day, and even the atmospheric conditions. The Vitamin D/UV Calculator Scientists at the Norwegian Institute for Air Research have devised a calculator that will take all those factors into consideration and estimate how many minutes of exposure you need for your skin to produce 25 mcg (the equivalent of 1,000 International Units) of vitamin D. It’s not the most user-friendly interface and it is very easy to enter the wrong information. But once you get past the technicalities, it’s very interesting to see how much the answers change when you vary the input. It is also not written for US cities so you can go to this page to find out latitude and longitude of many cites and enter the numbers manually. The easiest way may be to simply google “altitude of [your town]“. Remember to convert it to kilometers. One kilometer is about 3300 feet. If your latitude is 39 S, enter -39. If your longitude is 76 W, enter -76. You’ll also need to enter the time of day you are going out in the sun, expressed as UTC (Greenwich Mean Time). Here is a converter that will convert local time into UTC. The calculator uses a 24 hour clock, so hours from 1 PM to midnight are expressed as 13 to 24. The calculator also wants to know the thickness of the ozone layer. I suggest just setting this one to medium. Be sure to click the radio button next to the entries. They are often not automatically selected when you fill in the values. Keep in mind that the exposure times given are considered enough to maintain healthy vitamin D status. If you are starting out with a vitamin D deficiency, you might need more. | Vitamin D Dose Recommendations | |
|---|---|
| Age | Dosage |
| Below 5 | 35 units per pound per day |
| Age 5 – 10 | 2500 units |
| Age 18 – 30 | 5000 units |
| Pregnant Women | 5000 units |
| WARNING: There is no way to know if the above recommendations are correct. The ONLY way to know is to test your blood. You might need 4-5 times the amount recommended above. Ideally your blood level of 25 OH D should be 60ng/ml. | |
